The ABC of Computational Text Analysis
#4 Introduction to the Command-line
Alex Flückiger
Faculty of Humanities and Social
Sciences
University of Lucerne
24 March 2022
Recap last Lecture
- Successful installation? ✅
- Scripting 🎯
- automate, document, reproduce
- Any questions?
Outline
- learn principles of the shell 🏛️
- perform shell commands ▶️
- get practice by solving exercises 🏗️
How to get started
Open a Shell
macOS
- open
Terminal - shell type:
zsh
Windows
- open
Ubuntu 20.04 LTS - shell type:
Bash open Windows Command Prompt
Bourne-again Shell
Bash
- offers many built-in tools
- shell prompt
USER@HOSTNAME:~$
- home directory
~refers to/home/USER
- case-sensitive
- no feedback
- unless there is an issue
Unix Philosophy
Build small programs that do one thing
and do it
well. 🤓
Basic commands in Shell
example components of a command
command -a --long_argument FILE # non-working example commandrun command + help
echo "hello world" # print some text
man echo # get help for any command (e.g., echo)Where your files are stored
… and how to find them
hierarchical filesystem 🌲
- folders/directories
- files with a suffix
absolute path starting from top-level directory
- e.g.
/home/alex/KED2022/slides/KED2022_01.html
- e.g.
relative path looking from current directory
- e.g.
KED2022/slides/KED2022_01.html
- e.g.
.
├── README.md
└── lectures
├── images
│ └── ai.jpg
├── html
│ ├── KED2022_01.html
│ └── KED2022_02.html
└── md
├── KED2022_01.md
└── KED2022_02.md👍 Only relative paths work across systems
Important Places in your Filesystem
shortcut names of directories
.current dir..parent dir~home dir (e.g./home/alex)
find your files on Windows
/mnt/c/Users/YOUR_USERNAME/- shortcut with
documents
Navigating in a File System
pwd # show absolute path of current directory
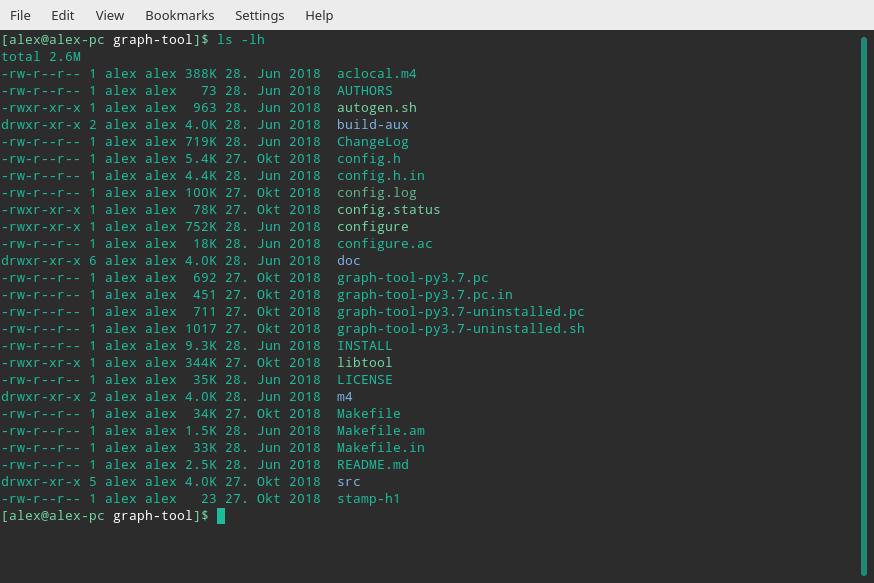
ls # list content of current directory
ls -lh # list with more information
ls dirname # list content of directory dirname
cd .. # change directory to go folder up
cd dir/subdir # go to folder dir/subdir (two folders down)when you are lost, open in file manager (GUI)
open . # open path in finder (macOS)
explorer.exe . # open Windows Explorer in WSL Ubuntu (Windows)Open Files
show within Shell
more text.txt # print content (space to scroll)
head text.txt # print first 10 lines of file
tail -5 text.txt # print last 5 lines of fileshow with default application (GUI)
open text.txt # macOS
wslview text.txt # WSL Ubuntu (Windows)Useful Key Actions
- autocompletion:
TAB - get last command: ⬆️
- scrolling:
SPACE - cancel
CTRL + C - quit:
qorCTRL + D
Creating, Moving and Copying
create files and directories
touch test.txt # create a new file
mkdir data # make a new directory
mkdir -p data/1999 # make a new directory with a subfoldercopy and move files
cp test.txt other/. # copy file into other folder, keep its name
mv test.txt other/new_name.txt # move or rename a fileRemoving Files
Watch out, there is no recycle bin. No way back!
rm old.txt # remove a file
rm -r old_data # remove a folder with all its filesIn-class: Exercises I
- Create a new directory called
tmp. - Change into that directory using
cdand print its absolute path usingpwd. - Use
touchto create a new file calledmagic.txtintmp. - Rename the file from
magic.txttoeasy_as_pie.txt. - Check out the helper page of
mvcommand. - Look around in the filesystem using
cdandls.
How is that useful? 🤔
We are getting there!
Wildcards
placeholders to match …
- any single character:
? - any sequence of characters:
*
mv data/*.txt new_data/. # move txt-files from to another subfolder
cp *.txt files/. # copy all txt-files in a single folderSearching
collect certain files only
ls *.txt # list all files with the suffix .txt (in current directory)find specific files
# search on filename
find /path/to/dir -name "*speech*" # find files in specific directory
locate -i pattern_1 pattern_2 # global search of files/folders
# search on content
grep -r "Europe" /path/to/dir # find all files containing X in a directory Expansion
batch processing with expansion
touch text_{a..c}.txt
# is equivalent to
touch text_a.txt text_b.txt text_c.txt
mkdir {2000..2005}{a..c}
# is equivalent to
mkdir 2000a 2000b 2000c 2001a 2001b 2001c ...Operators
Combining Commands
use shell operators to …
- redirect output into file (overwrite):
> - append to existing file:
>> - stream to next command:
|(pipe)
echo 'line 1' > test.txt # write into file
more test.txt | tail -1 # pass output to next command Merging Files
cat part_1.txt part_2.txt # concatenate multiple files
cat *.txt > all_text.txt # merge all txt into a single oneConventions 🙏
- no spaces/umlauts in names
- alphanumeric, underscore, hyphen, dot
- files have a suffix, folders don’t
text_1.txtvs.texts
- descriptive file names
SOURCE/YEAR/speech_party_X.txt
- don’t modify the raw data
Writing a runnable Script
Example script:
find_all_pdf.sh
#!/bin/sh
echo "This is a list of all PDFs on my computer:"
locate -i /home/*.pdf- file with suffix
.sh- one command per row
#precedes comments
- start script with Shebang
#!/bin/sh - execute with
bash SCRIPTNAME.sh
The beauty of scripting is automation. ⚡
Assignment #1 ✍️
- get/submit via OLAT
- starting tonight
- deadline: 31 March 2022, 23:59
- discuss issues on OLAT forum
- ask friends for support, not solutions
Questions?
In-class: Exercises II
Create a new file with
touch.Write the following content into that file, one line at a time using the append operator:
How about making programming a little more accessible? Like: from human_knowledge import solutionMake sure that the content was written into that file using
more.
In-class: Exercises III
Navigate up and down in in your filesystem using
cdand list the respective files per directory withls. Where can you find your personal documents? Print the absolute path withpwd.
A hint to Windows users as they are working in a Ubuntu subsystem, have a look at:/mnt/c/UsersRead
man lsand write anlscommand that lists your documents ordered- by recency (time)
- by size
Use the
|and>operators to write the 3 “last modified” files in your documents folder into a file calledlast-modified.txton your desktop (desktop is also a directory). It is a single command performing multiple operations, one after another.
Additional Resources
useful primers on Bash
- Cheatsheet for this course
- The Programming Historian
- DigitalOcean